

In 1915, the German high command began to contemplate its next major strategic move to turn World War I in its favour. Unknown to the French in Verdun, decisions were being taken within the German high command that would eventually make this relaxed existence nothing but a haunted and shattered memory. This was reflected not only in an encroaching complacency amongst the French garrison, but also in the stripping of many of the fortress’ guns to provide artillery for batteries elsewhere. Apart from such fiery interruptions, however, Verdun was actually one of the quieter sectors on the front. The latter included a fearsome pounding of Forts Douaumont and Vaux by 420mm howitzers, which succeeded in creating some significant external damage but without disabling critical French gun emplacements. While fighting continued around Verdun, the town and its fortresses themselves came in for German attention, chiefly in the form of aerial and artillery bombardment. The German capture of the feature brought vigorous French counter-attacks in the early months of 1915, but while infantry combat largely ground to a halt by 4 March, mine warfare continued for months to come, as each side attempted to secure the feature. Twenty-four kilometres (15 miles) to the west of the town, the elevated Butte de Vauquois was similarly contested. A French counter-attack from 17 February 1915 reclaimed much of the ridge, although some eastern parts of the feature remained in German hands almost until the end of the war.

The Germans also managed to capture the Les Éparges ridge, a strategically useful piece of high ground 24km (15 miles) to the south-east of Verdun. The outlying Fort Troydon and Fort Camp des Romains were destroyed and captured respectively, and two of the main railway lines into Verdun were cut, leaving the town with just a single road and a narrow-gauge railway track from Bar-de-Luc as its main routes of supply from the west. Yet the Germans did succeed in weakening Verdun’s defensive integrity. Thankfully for the French, Verdun’s commander disobeyed the order.
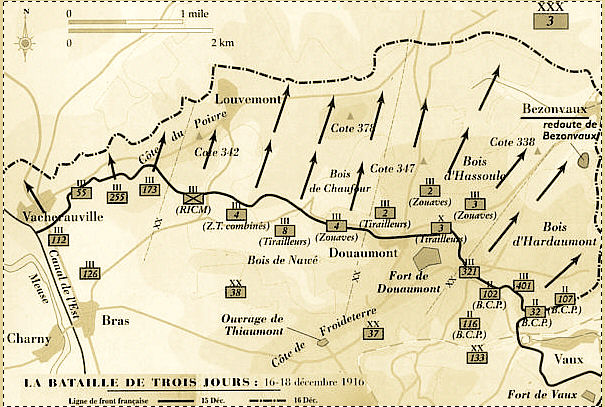
This effort came close to success, not only because the German pincers nearly closed around Verdun, but also because Joffre had actually ordered the town to be abandoned. In September 1914 German forces had attempted to encircle and cut off the fortified town. Occupying a bulging salient, it was actually one of the most defensible French positions along the entire frontline, although not everyone on the French staff appreciated that fact. The garrison of the Verdun region numbered 65,000 men. It featured a total of nineteen major forts, armed with concrete- and metal-emplaced 155m and 75mm cannon and machine guns, with a total of forty-seven armoured observation posts set about the landscape. Fought between the German and French armies from February to December 1916, this brutal battle of attrition claimed one million casualties with 300,000 killed.īy the time major European war broke out in 1914, Verdun cast an imposing shadow over the French landscape.

Though it was described at the time as “the war to end all wars,” the scar that World War I left on the world was anything but temporary.The Battle of Verdun was the longest single battle during the First World War and one of the bloodiest in human history. The technology that the war had generated would be used in the next world war just two decades later. Though the world vowed never to allow another war like it to happen, the roots of the next conflict were sown in the Treaty of Versailles, which was viewed by Germans as humiliating and punitive and which helped set the stage for the rise of fascism and World War II. “Shell shock” and the aftereffects of gas poisoning would claim thousands more lives. Revolution had broken out in Germany, Russia, and other countries. on November 11, 1918.īy then, the world was in the grips of an influenza pandemic that would infect a third of the global population. Battles like the Battle of Verdun and the First Battle of the Somme are among the deadliest in the history of human conflict.Īided by the United States, the Allies finally broke through with the Hundred Days Offensive, leading to the military defeat of Germany. Unauthorized use is prohibited.ĭespite advances like the use of poison gas and armored tanks, both sides were trapped in trench warfare that claimed enormous numbers of casualties.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
